Did you know that the World Economic Forum estimates that smart manufacturing could add over $14 trillion to the global economy by 2030? This figure highlights the profound influence of digital transformation on the manufacturing sector. As we navigate the realm of smart manufacturing, it is evident that this transformation transcends a fleeting trend, marking a critical shift towards automation and the assimilation of cutting-edge technologies. Smart manufacturing, driven by Industry 4.0, employs tools like the Internet of Things (IoT) and data analytics, setting the stage for unparalleled efficiency and innovation in production methodologies.
Our exploration into the core of smart manufacturing reveals its crucial role in redefining the operational dynamics of industries worldwide. The benefits are substantial, ranging from enhanced productivity to superior product quality. To fully grasp and incorporate these transformative changes, enterprises are advised to seek out specialized guidance through valuable resources and support.
Key Takeaways
- Smart manufacturing significantly impacts the global economy.
- Digital transformation is essential for competitive advantage.
- Automation streamlines production processes.
- IoT and data analytics drive efficiency in manufacturing.
- Industry 4.0 represents a new era for production systems.
What is Smart Manufacturing?
Smart manufacturing heralds a paradigm shift in the production domain, integrating cutting-edge technologies to elevate operational efficacy. It encompasses a broad spectrum of methodologies and tools, aimed at boosting efficiency, adaptability, and responsiveness in manufacturing endeavors. As industries increasingly adopt digital transformation, the advent of smart factories emerges as crucial, demonstrating the potential of interconnected systems to significantly enhance productivity and effectiveness.
Definition and Overview
At its essence, smart manufacturing leverages intelligent systems, including the Internet of Things (IoT), data analytics, and automation, to forge interconnected manufacturing environments. This pioneering strategy empowers entities to harness real-time data, facilitating expedited decision-making and optimized resource allocation. By metamorphosing traditional production lines into smart factories, corporations can attain superior agility and competitiveness within a rapidly shifting market.
Key Components of Smart Manufacturing
Several pivotal components constitute the bedrock of smart manufacturing. These elements synergistically collaborate to establish interconnected and efficient production processes:
- Smart Factories: Facilities equipped with advanced technologies to facilitate communication between machines and systems.
- Connected Devices: Sensors and devices that collect and transmit data, enabling continuous monitoring of production activities.
- Real-Time Monitoring Systems: Tools that allow manufacturers to track performance metrics instantly and respond to anomalies without delay.
In conclusion, the core of smart manufacturing resides in its capability to propel digital transformation within the production sector. As enterprises continue to evolve, comprehending the importance of these technologies will be critical for enduring growth and sustainability. For further insights on embarking on your journey in this digital epoch, visit understanding key concepts of business registrations.
Benefits of Smart Manufacturing
Smart manufacturing revolutionizes traditional production methodologies, transforming them into highly efficient and profitable systems. Through the integration of advanced technologies, enterprises can significantly improve their operational frameworks. This leads to notable enhancements in productivity, cost reduction, and product quality.
Increased Efficiency and Productivity
The core benefit of smart manufacturing resides in its capacity to elevate operational efficiency and productivity. Automation and real-time data analysis streamline processes, reducing downtime and expediting production. Factories equipped with cutting-edge technologies can promptly adapt to shifting demands, thereby ensuring maximum output.
Cost Reduction Strategies
Smart manufacturing introduces various cost reduction strategies that significantly impact profitability. Techniques such as optimized resource allocation and waste minimization not only reduce operational costs but also enhance profitability. Companies adopting these strategies often experience substantial savings, bolstering their competitive position in the market.
Enhanced Product Quality
Ensuring high product quality becomes more straightforward with the implementation of smart manufacturing systems. Precise monitoring and control mechanisms enable manufacturers to identify deviations early in the production process. This leads to improved accuracy, allowing companies to consistently deliver superior products that meet customer expectations. For further insights on transforming production with smart solutions, explore smart manufacturing strategies.
Technologies Driving Smart Manufacturing
The metamorphosis of smart manufacturing hinges on the advent of cutting-edge technologies, which significantly boost productivity and efficiency. Paramount among these are the Internet of Things (IoT), Artificial Intelligence (AI), machine learning, robotics, and automation. These innovations are pivotal in revolutionizing traditional manufacturing methodologies.
Internet of Things (IoT) in Manufacturing
IoT devices enable the interconnection of machines and systems, facilitating unimpeded communication and data exchange. This connectivity empowers real-time monitoring and expedites the identification of inefficiencies. By integrating IoT solutions, enterprises acquire profound insights into operational performance, thereby enabling more astute decision-making.
Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning
AI and machine learning technologies are instrumental in optimizing processes through predictive analytics. These tools scrutinize extensive datasets to forecast equipment malfunctions and streamline production. The incorporation of AI empowers manufacturers to execute intelligent adjustments based on data-driven insights, thereby enhancing operational outcomes.
Robotics and Automation
Advancements in robotics have profoundly altered the manufacturing paradigm. Automated systems undertake repetitive tasks, thereby augmenting both speed and precision. As manufacturers embrace automation, they mitigate physical strain on employees and diminish labor expenses. The deployment of robotics escalates production capacity and supports a more dynamic manufacturing environment.
Technologies such as IoT, AI, machine learning, and robotics are indispensable to the advancement of smart manufacturing. For deeper insights into these innovations, refer to smart manufacturing resources. Acquaintance with these technologies empowers businesses to excel in an increasingly automated milieu. Automation not only amplifies productivity but also cultivates an environment of innovation within the manufacturing sector, promoting continuous enhancement and adaptation.
As industries evolve, it is imperative to remain abreast of emerging technological trends. The synergy of IoT and AI ensures manufacturing facilities remain competitive and responsive to market exigencies. For additional information on embracing automation, explore franchise opportunities that facilitate businesses aiming for expansion through technological advancements.
Challenges in Implementing Smart Manufacturing
The transition to smart manufacturing is fraught with obstacles that necessitate a thorough understanding. Initial costs, workforce resistance, and data security are paramount concerns. These factors are critical to the success of any organization embarking on this transformative journey.
High Initial Costs
Adopting cutting-edge technologies and upgrading equipment entails substantial financial outlays. The initial investment required to modernize manufacturing infrastructure is a significant hurdle. Overcoming these financial barriers is imperative for organizations aiming to fully integrate smart manufacturing.
Resistance to Change in Workforce
Workforce resistance is another formidable challenge. Employees may harbor concerns about job security and the need for new skill sets. Effective communication and training are essential to alleviate these fears. This approach fosters a culture that values innovation and change.
Data Security Concerns
The advent of advanced technologies heightens the stakes for data security. Ensuring the protection of sensitive information from cyber threats is paramount. Implementing stringent cybersecurity measures is vital to safeguard data integrity and maintain stakeholder trust.
Smart Manufacturing and Sustainability
Smart manufacturing is instrumental in fostering sustainable practices across diverse sectors. It harnesses cutting-edge technologies and data-driven methodologies to significantly bolster waste reduction and energy efficiency. These advancements are pivotal in harmonizing production methodologies with environmental benchmarks and objectives.
Reducing Waste in Production
The core benefit of smart manufacturing lies in its capacity to diminish waste. It employs various techniques, including:
- Adoption of lean manufacturing principles to refine production workflows.
- Employment of predictive analytics to forecast demand, thus curtailing overproduction.
- Optimization of material usage through advanced design methodologies.
These methodologies not only facilitate effective waste minimization but also contribute to a more sustainable manufacturing paradigm by optimizing resource utilization.
Energy Efficiency Practices
Energy efficiency is a cornerstone of sustainable manufacturing. Strategies to enhance energy utilization encompass:
- Deployment of IoT devices for real-time monitoring of energy consumption in machinery.
- Integration of renewable energy sources, such as solar or wind, into production facilities.
- Implementation of automation to optimize energy consumption during operational periods.
These practices not only lower operational expenses but also underscore a commitment to environmental stewardship within the manufacturing domain. Smart manufacturing thus heralds a greener epoch.
Case Studies of Smart Manufacturing Success
An examination of real-life examples of smart manufacturing success stories unveils profound insights into the adoption of advanced technologies across various industries. These sectors have embraced innovative methodologies, leading to substantial improvements in productivity and competitiveness.
Leading Industries Adopting Smart Manufacturing
Several industries are pioneering the adoption of smart manufacturing, acknowledging the imperative for transformation. Key sectors include:
- Aerospace
- Automotive
- Electronics
- Pharmaceuticals
Each of these industries has demonstrated a steadfast commitment to innovation, effectively integrating smart technologies into their operations.
Specific Company Examples
General Electric has made significant strides in their manufacturing processes through the implementation of IoT technologies. These advancements have resulted in enhanced efficiency and a reduction in downtime. Similarly, Siemens has led the charge in smart manufacturing initiatives, focusing on automation and data analytics to optimize production.
To delve deeper into smart manufacturing success stories, companies are increasingly sharing their experiences. These narratives underscore the benefits of aligning operations with smart technologies, fostering innovation and setting benchmarks for industry adoption.
Future Trends in Smart Manufacturing
The evolution of smart manufacturing is propelled by continuous technological progress. The trajectory of this evolution is promising, with industries harnessing AI advancements and big data to refine operations and decision-making processes. These emerging trends are fundamentally altering the management and optimization of production processes.
Advancements in AI and Machine Learning
Artificial intelligence and machine learning are pivotal in revolutionizing manufacturing. As these technologies evolve, they empower machines to autonomously learn and adapt. This evolution results in substantial enhancements across various domains:
- Predictive analytics that diminish downtime by foreseeing machine malfunctions.
- Automated quality control mechanisms that elevate product uniformity.
- Optimized production schedules that maximize resource efficiency.
The Role of Big Data Analytics
Big data analytics is indispensable in deciphering the vast amounts of data generated during manufacturing. Through the analysis of this data, companies can glean insights that propel efficiency and innovation. The influence of big data in manufacturing is evident in several areas:
- Unveiling trends and patterns for enhanced demand forecasting.
- Improving supply chain transparency among diverse stakeholders.
- Augmenting customer experiences through personalized product offerings.
Integration with Supply Chain Management
The synergy between smart manufacturing and supply chain management elevates operational efficiency and transparency to unprecedented levels. Central to this synergy is the exchange of real-time data. Such data exchange empowers businesses to refine their operations, ensuring the availability of products at optimal times. This heightened visibility across the supply chain facilitates superior demand forecasting and inventory management, thereby fostering supply chain optimization.
Real-Time Data Sharing
The exchange of real-time data among supply chain stakeholders is paramount in contemporary manufacturing. Immediate access to pertinent information enables companies to rapidly respond to market fluctuations. Such agility can result in:
- Reduced inventory expenses
- Decreased stockout occurrences
- Enhanced customer satisfaction
The deployment of integrated systems that facilitate real-time data exchange empowers each segment of the supply chain to make informed decisions. A harmonized approach enhances transparency and promotes a more streamlined process overall.
Improved Collaboration among Stakeholders
Effective stakeholder collaboration is indispensable for the success of supply chains. When manufacturers, suppliers, and distributors collaborate, they can harness insights from shared data, yielding mutually advantageous outcomes. Such collaboration encompasses:
- Joint demand planning
- Coordinated logistics strategies
- Shared risk management plans
These collaborative endeavors facilitate strategic decision-making that aligns with the objectives of all stakeholders. By embracing cutting-edge technologies and cultivating open communication channels, stakeholders can forge a more resilient supply chain. This chain is adept at navigating challenges and seizing opportunities. For those aiming to enhance their professional competencies, exploring top educational resources for continuous learning and development is advisable.
Smart Manufacturing in Different Industries
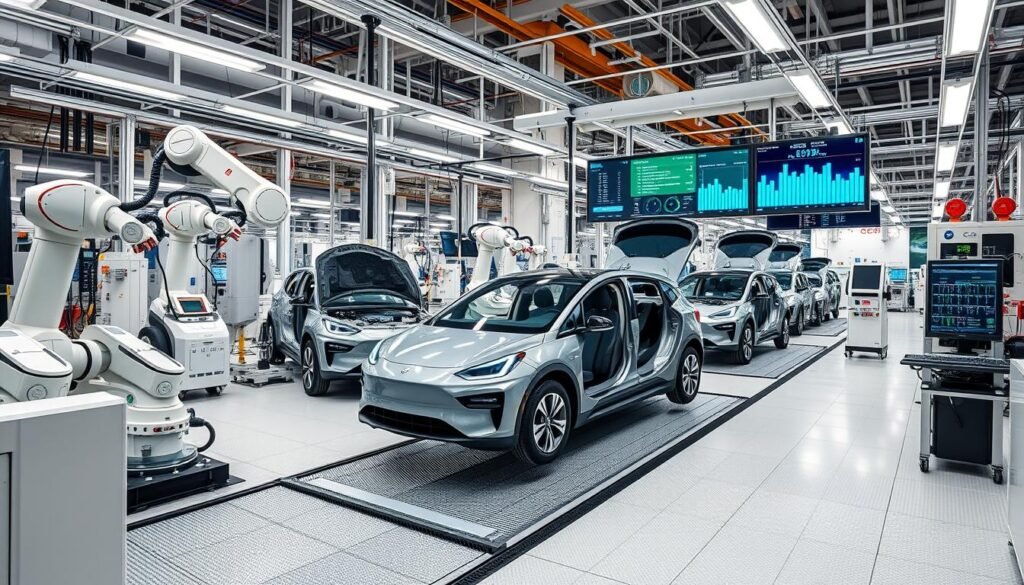

Diverse sectors are adopting specialized smart manufacturing methodologies to elevate their operational efficiency and product diversity. Through technological advancements, the automotive, aerospace, and consumer electronics sectors are undergoing significant transformations. These innovations are reshaping the landscape of manufacturing, enabling industries to achieve unprecedented levels of productivity and innovation.
Automotive Industry Innovations
The automotive sector is at the vanguard of technological advancements. Integration of smart robotics into assembly lines has significantly enhanced efficiency and precision. The advent of autonomous vehicles and connected technologies is revolutionizing transportation, offering safer and more environmentally friendly options. Leading brands such as Tesla and Ford are pioneering the use of data analytics to optimize production processes, setting new benchmarks for the industry.
Aerospace and Defense Applications
In the aerospace and defense sectors, precision and adherence to stringent regulations are paramount. Smart manufacturing enables the creation of components that meet the most exacting aerospace standards. Lockheed Martin and Boeing exemplify companies leveraging smart technology to refine quality control and expedite production timelines, showcasing the sector’s commitment to excellence.
Consumer Electronics Advancements
The consumer electronics industry has embraced automated assembly lines to enhance productivity and reduce time-to-market. Industry giants such as Apple and Samsung are at the forefront of innovation, leveraging smart manufacturing to create cutting-edge designs and functionalities. Automation not only accelerates production but also elevates product quality, catering to the evolving expectations of consumers.
Skills Needed for the Workforce of Tomorrow
The advent of smart manufacturing necessitates a paradigm shift in the requisite workforce skills. Training programs, designed to equip employees with the competencies demanded by this evolving landscape, are paramount for success. A forward-thinking approach to workforce development is imperative, ensuring professionals are adept to navigate the future’s manufacturing challenges.
Training and Workforce Development
Training programs are instrumental in cultivating the competencies essential for contemporary manufacturing roles. Companies must commit to comprehensive training, integrating emerging technologies and digital tools. Successful training initiatives should include:
- Hands-on experience with the latest manufacturing technologies
- Workshops and seminars that focus on critical thinking and problem-solving skills
- Collaboration with educational institutions to create tailored training programs
Embracing Lifelong Learning
Adapting to rapid advancements requires a culture of lifelong learning. Continuous education enables workers to effectively adapt to new manufacturing practices. Strategies to foster lifelong learning include:
- Providing access to online courses and certification programs
- Encouraging mentorship and peer-to-peer knowledge sharing
- Establishing a supportive environment that values curiosity and innovation
The Role of Data Analytics
Data analytics in manufacturing profoundly impacts the optimization of processes and performance enhancement within organizations. By comprehensively understanding production metrics, manufacturers can uncover insights that catalyze efficiency and facilitate predictive maintenance strategies. This section delves into the advantages of employing data analytics within the manufacturing sector.
Understanding Production Metrics
Production metrics act as pivotal indicators, enabling manufacturers to monitor diverse operational facets. These metrics encompass:
- Overall Equipment Effectiveness (OEE)
- Throughput rates
- Defect rates
- Cycle times
Through data analytics, corporations can scrutinize these metrics in real-time, discerning patterns that underpin strategic decision-making. This methodology cultivates a culture of perpetual enhancement, empowering organizations to refine their production methodologies and elevate output.
Predictive Maintenance and Performance Optimization
Adopting predictive maintenance substantially diminishes equipment downtime in manufacturing. By harnessing sophisticated algorithms and machine learning paradigms, entities can forecast impending malfunctions beforehand. This anticipatory strategy ensures maintenance activities are optimally scheduled, thereby curtailing disruptions to production timetables. The principal benefits include:
- Lower maintenance expenditures
- Extended equipment longevity
- Enhanced operational availability
Integrating data analytics into predictive maintenance frameworks significantly bolsters performance optimization across the manufacturing domain, resulting in superior reliability and efficiency.
Government and Policy Initiatives

The pivotal role of government support in propelling smart manufacturing across diverse sectors cannot be overstated. Systematic investments, coupled with the implementation of astute smart manufacturing policies, catalyze innovation and expedite the shift towards contemporary production methodologies. This discourse explores the initiatives aimed at fortifying these advancements.
Support for Smart Manufacturing Initiatives
Multiple programs are in place to nurture the expansion of smart manufacturing. These encompass funding opportunities, grants, and technical support provided by both federal and state agencies. Critical support mechanisms include:
- Investment tax credits designed to alleviate the financial strain on entities embracing new technologies.
- Public-private partnerships that foster collaboration between governmental entities and manufacturing enterprises.
- Training initiatives aimed at equipping the workforce with the necessary skills for smart manufacturing tools.
Regulations Impacting Adoption
The realm of smart manufacturing is further influenced by a myriad of regulations. Adherence to these regulations can elevate safety standards, enhance operational efficiency, and promote sustainable practices. Key regulations encompass:
- Standards for data security aimed at safeguarding sensitive information against cyber threats.
- Environmental regulations focused on minimizing waste and optimizing energy consumption.
- Health and safety guidelines ensuring a secure working environment during the integration of new technologies.
Smart Manufacturing and Cybersecurity
The advent of smart technologies in manufacturing heralds a new era of efficiency and innovation. However, it also introduces profound cybersecurity challenges. The heightened connectivity of these systems amplifies their susceptibility to cyber threats, underscoring the imperative of robust data protection measures. It is incumbent upon businesses to proactively safeguard sensitive information and to deploy comprehensive cybersecurity strategies.
Protecting Sensitive Data
Ensuring cybersecurity in manufacturing necessitates the development of frameworks that safeguard critical data assets. Initially, pinpointing sensitive data assets enables companies to concentrate their protective efforts. Encrypting data during transfers and securely storing it diminishes the likelihood of unauthorized access, thereby mitigating risks.
Best Practices for Cybersecurity
Adopting best practices is crucial for maintaining cybersecurity in smart manufacturing settings. Consider the following recommendations:
- Regularly update software to patch vulnerabilities.
- Train employees on the importance of cybersecurity awareness.
- Establish access control measures to limit data exposure.
- Conduct regular security audits to identify weaknesses.
- Utilize firewalls and intrusion detection systems actively.
By adhering to these best practices, manufacturers can significantly bolster their data protection efforts. This, in turn, diminishes the risks associated with cyber threats and cultivates a secure operational environment.
Smart Manufacturing and Supply Chain Resilience
Smart manufacturing is pivotal in fortifying supply chain resilience. Through the integration of cutting-edge technologies, entities can construct resilient supply chains, capable of enduring diverse disruptions. This methodology ensures that corporations maintain their competitive edge and adaptability within the dynamic marketplace.
Building Robust Supply Chains
To forge resilient supply chains, enterprises must concentrate on several critical strategies:
- Diverse Suppliers: Collaborating with multiple suppliers diminishes the perils of dependency on a solitary source.
- Real-Time Monitoring: Employing IoT devices facilitates perpetual surveillance of supply chain operations, thereby augmenting decision-making efficacy.
- Risk Assessment: Periodic evaluation of potential risks and the formulation of contingency plans are indispensable for sustaining equilibrium.
Agile Manufacturing Practices
Agile manufacturing practices are instrumental in bolstering supply chain resilience. By embracing flexible methodologies, corporations can promptly respond to market fluctuations and disruptions. The hallmark of agile manufacturing encompasses:
- Rapid Prototyping: The expedited creation of prototypes accelerates the introduction of new products to the market.
- Cross-Functional Teams: Promoting interdepartmental collaboration stimulates innovation and enhances operational efficiency.
- Continuous Improvement: Cultivating a culture of perpetual assessment leads to the refinement of processes and productivity enhancement.
Conclusion: Embracing the Future of Production
In the realm of manufacturing, the advent of smart manufacturing heralds a paradigm shift towards unparalleled production efficiency. This discourse has delved into the myriad benefits, encompassing enhanced productivity, the integration of cutting-edge technologies such as IoT and AI, and the imperative for robust cybersecurity measures. These components underscore the necessity for embracing smart manufacturing practices to excel in the fiercely competitive marketplace.
Summary of Key Points
The amalgamation of smart manufacturing technologies not only augments operational efficacy but also synergizes with environmental sustainability by minimizing waste and promoting energy conservation. Industries spanning from automotive to aerospace are witnessing tangible benefits, illustrating the pivotal role of adaptable and resilient supply chains in achieving success. The insights shared delineate a clear trajectory towards leveraging these advancements to fortify production ecosystems.
Call to Action for Businesses
It is imperative for businesses to act with alacrity. The adoption of smart manufacturing is not an option but a critical imperative for those aspiring to maintain their competitive edge. Enterprises must commit to workforce development, enhance data analytics capabilities, and embrace innovative technologies to fully capitalize on the potential of smart manufacturing. Let us collectively navigate these transformations, embracing the opportunities that the future presents.